|
| |
 The moon is a rocky, cratered place, roughly a quarter the size of Earth and an average of 238,855 miles away. The Moon can be seen with the naked eye most nights as it traces its 27-day orbit around our planet. The moon is a rocky, cratered place, roughly a quarter the size of Earth and an average of 238,855 miles away. The Moon can be seen with the naked eye most nights as it traces its 27-day orbit around our planet.
"Lunar Reference Time" is a new time zone used exclulsively for the Moon. Time is the measurement of a period of specified duration. The lunar reference time does not depend on the rotation of the Earth or the solar time, it's just a unique time scale used to reference all activities on the Moon surface.
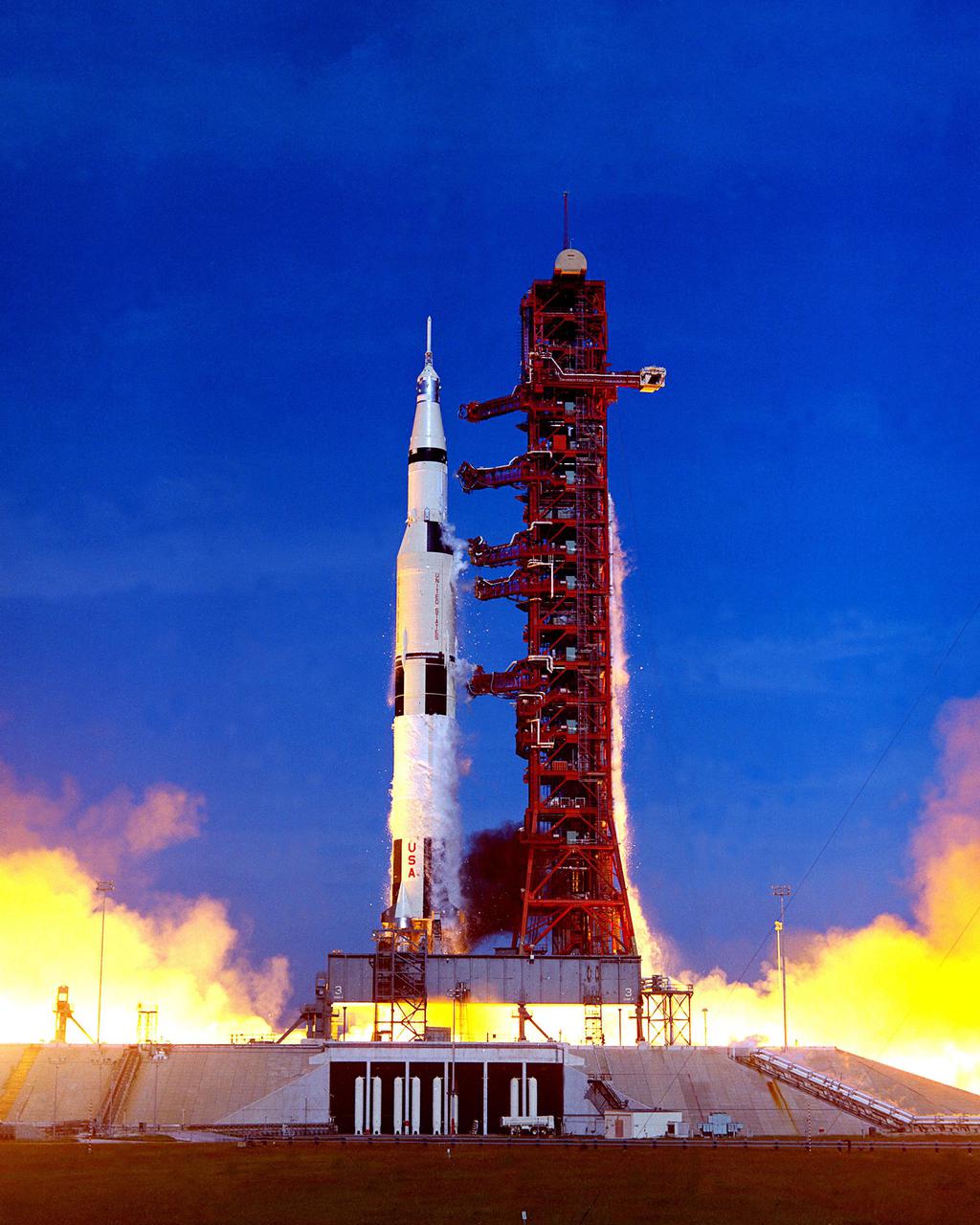
Shown at right is The Apollo 15 Saturn V Space Vehicle soars into the skies after liftoff at Launch Pad 39A marking the beginning of NASA's fourth Manned Lunar Landing Mission. The astronauts aboard are David R. Scott, commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module pilot; and Alfred M. Worden Jr., Command Module pilot. The landing site for the Lunar Module was the Hadley-Apennine area of the Moon, about 465 miles north of the Lunar Equator. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was used for the first time. |
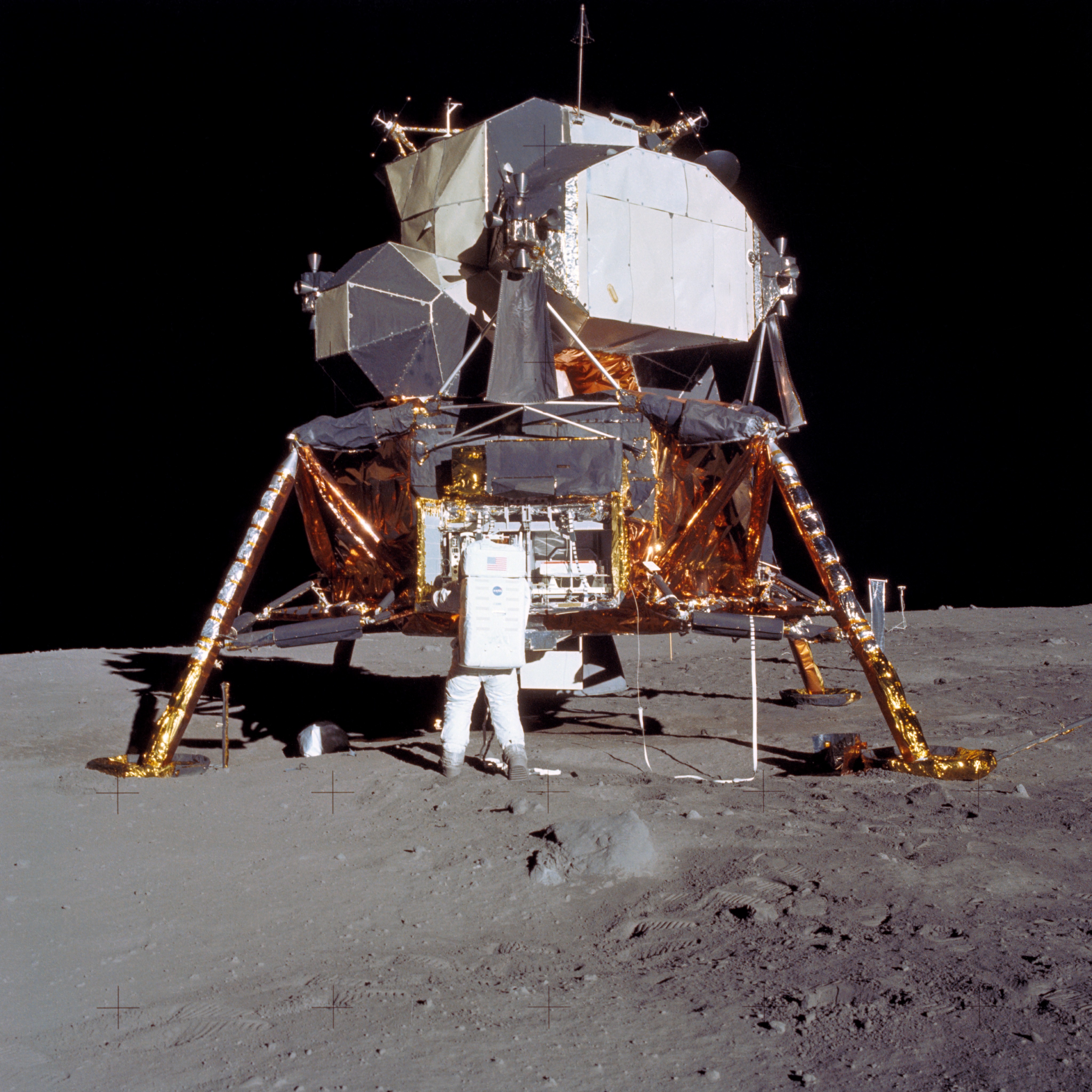 |
All nations and individuals who venture to the Moon will use this standardized "Lunar Reference Time". Having a Moon time zone will make things easier for all.
This universal time is used in astronomy and navigation on the Moon. The lunar reference time is a time scale that has no dependency of the rotation of the earth or any other planetary body.
A lunar month is the time it takes the Moon to pass through all of the Moon phases, measured from one New Moon to the next New Moon. This is a measurement of how the Moon acts in relationship to the earth, not a measurement of time on the Moon.
The Lunar Date (LD) is a system of numbered days. Each day number 1 is followed by two, then four, making up a cycle lasting about 29 days. The lunar reference time is a time system that divides the calendar month into 29.5 days and allows each day to be given a unique name and number. |
|
|
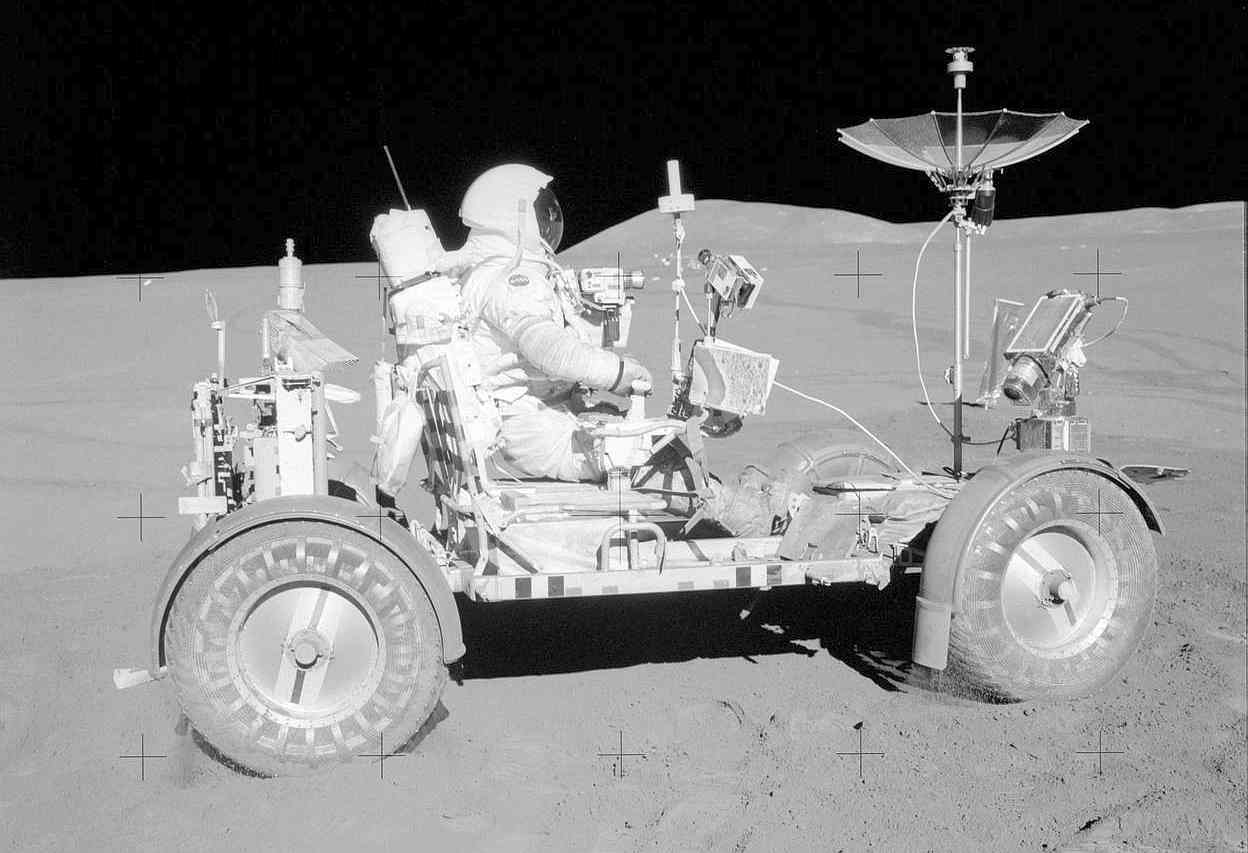 |
| Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, is seated in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. |
 |
Space Travel - Most of us will never travel to space, but we can virtually. First take a tour of NASA’s offices. Then relive the last lunar missions and moon walks in stunning HD.
On December 7, 1972, NASA launched Apollo 17, a lunar mission crewed by Eugene Cernan, Ronald Evans, and Harrison Schmitt. It would be the last time humans traveled beyond low Earth orbit, the last time man landed on another celestial body, and the last time man went to the moon. The Last Steps uses rare, heart-pounding footage and audio to retrace the record-setting mission. |
|
|
|
|


 The moon is a rocky, cratered place, roughly a quarter the size of Earth and an average of 238,855 miles away. The Moon can be seen with the naked eye most nights as it traces its 27-day orbit around our planet.
The moon is a rocky, cratered place, roughly a quarter the size of Earth and an average of 238,855 miles away. The Moon can be seen with the naked eye most nights as it traces its 27-day orbit around our planet.